:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-14050070541-0fc96b82fdc54287bf3bbce3ba323342.jpg)
New 2024 Approved All About Anime Dubbing

All About Anime Dubbing
All about Anime Dubbing

Shanoon Cox
Mar 27, 2024• Proven solutions
Anime might have been originated from Japan, but today it has become a worldwide phenomenon with millions of fans out there. Since most of the anime series are in Japanese, they are dubbed in different languages for their global audience. Though, anime dubbing is an art in itself as it takes a lot of effort to provide a seamless entertainment experience to others. In this post, I’m going to make you familiar with the process that goes behind anime dubbing and how you can master it in no time.

- Part 1: What is the Art of Anime Dubbing?
- Part 2: Why is Voicing Important in an Anime?
- Part 3: What is the Process of Anime Dubbing?
- Part 4: Is Anime Dubbing Enjoyable or Painful?
- Part 5: Anime Dubbing Tips for Beginners
What is the Art of Anime Dubbing?

http://animeyourway.blogspot.com/
There are tons of anime out there, but most of them are originally made in Japanese. To make them appealing to an international audience, the concepts of dubbing and subbing are implemented. In subbing, we simply add subtitles to the scene by placing its strip at the bottom, which is comparatively easier.
On the other hand, Anime dubbing is a more complex process in which the original soundtrack in Japanese is first removed from the video. Now, a script is designed for the other language (like English) in which the video has to be dubbed. Afterward, voiceover artists would match the dialogues with the original pace of the video to attain flawless dubbing results. Now, the audience of the second language can also watch the anime with the dubbed soundtrack instead of the Japanese.
In some cases, even after dubbing, subtitles are also added in post-production to get better results.
Why is Voicing Important in an Anime?

Anime is an art-form and hence, it is should be treated creatively when transitioning into different cultures. The first generation of anime traces to the 1910s in Japan while they became mainstream with Astro Boy that was a hit not only in Japan but in the US as well. Needless to say, the anime industry has grown drastically with over $17 billion worth worldwide.
That’s why it has become more important than ever to focus on anime dubbing and make the content appealing to a vast audience. Too many times, while dubbing, the original nature of a character is lost due to the improper voice transition. Sometimes, there are edits in the script to match the pace of the scene that ends up changing the meaning drastically.
Therefore, to make sure the true essence of the anime is maintained, the concept of voice interpretation is implemented. In this, voiceover artists are taught about their characters and their nature. Instead of bringing their own flair while recording, they are encouraged to voice their characters instead.
What is the Process of Anime Dubbing?
Now when you know the importance of anime dubbing, let’s get to know about the process in detail. Although the overall process can be implemented differently in various countries and studios, the following steps are mostly followed by professionals.
Step 1: Transitioning and Translation
This is the foundation of anime dubbing as it helps us in scriptwriting and voiceover. Firstly, the anime is studied by the team, which includes native Japanese experts. For instance, if the anime is about Japanese history or its pop culture, then an expert from the related field is asked to join.
Furthermore, all the dialogues are transcribed and further translated by professionals. To make sure that no cultural norms are lost in the process, a group of people is invited to work on this. If the anime is about pop culture, then it can be a bit tough since some dialogues might lose the original meaning in the translation.
Step 2: Scripting and Adaptation
A mere translation of the anime is not enough as it is needed to fit the scene and should have a flawless transition. For this, scriptwriters take the translated document (for instance, Japanese to English translated version) and start developing a script for that. They will watch the scene simultaneously and would work with voiceover artists as well. In this way, we can avoid any delay or rapid movement between the picture and voiceover audio.
- The new dialogues should be spoken in the same way so that the original speech and the voiceover should be matched.
- A lot of sentences have to be reconstructed entirely since Japanese grammar is pretty different than English. Sometimes, a single word in Japanese might mean a whole sentence in English. This means we need to write the script while matching the pace of the scene and keeping the meaning intact (which can be pretty challenging).
- Scriptwriters need to focus on the way a sentence is delivered and conveyed. If you are not careful, then you will lose out on certain nuances.
- To get an ideal script, you might need to watch the anime and deliver your dialogues back-and-forth. Writers are encouraged to be more adaptive and keep the cultural knowledge of their audience in mind as well.
- If the anime is deeply rooted in Japanese cultural norms that you know your audience won’t understand, then you can abandon it while still being faithful to the original material. For instance, Shin-chan had too many Japanese norms and thus it was re-written in English to include more local terms.
Step 3: Recording and Finishing
After completing the scriptwriting, recording artists work on it to give it a final touch. Although it is recommended for all recording artists to do their voice work together for a seamless amalgamation, sometimes they record their dialogues separately as well.
The recording artists are encouraged to do their bit of research and are made familiar with the anime. During the recording process, artists focus on the “matching flap” movement, which means their dialogues should match with the movement of their character’s lips. For this, they can fasten or slow their speed of dialogue delivery or add bits and pieces in between to give it a personal character.
While it is not possible to be entirely accurate and match the pace, artists try their best by looking at the video while delivering their dialogues. Some mistakes and flubs are bound to happen in the process, but that is what makes anime dubbing so hilarious and creative.
Is Anime Dubbing Enjoyable or Painful?
This is something that a lot of anime fans would like to ask voiceover professionals. Well, it would be subjective and depend on the anime as well as the professionals working on it.
In most of the cases, the process is pretty enjoyable if the artists and writers are fans of anime. Yes, the process can be a bit tedious, but that is the demand of this challenging profession altogether.
Michael Lindsay, who was widely appreciated for his work in the Marmalade Boy, admits how tough the job can be. It requires a lot of rework and the voiceover artists need to go back-and-forth to get the right pace.
Olivia Venegas, who has been a part of the anime dubbing industry for over a decade, admits how the process has changed. Now, production houses are more focused on creating a “localized” version of the anime that their audience can understand instead of keeping it rigid to their original material.
Overall, the change in the anime dubbing process and the presence of better technology has certainly made it more fun and less painful.
Anime Dubbing Tips for Beginners
If you are just starting your career in anime dubbing and would like to improve your work, then consider these expert tips.
- To start with, do your bit of research and make sure you understand the Japanese culture. If the anime is about history or a cultural phenomenon, then get to know about it so that you won’t miss any nuance.
- If you are a voiceover artist, then sit with the scriptwriter during the translation and writing process. This will help you understand their writing process and you can also give suggestions regarding voiceover.
- Focus on your speech and the pace while recording every word. At times, we are needed to eat some words or have to stretch them to match with the movement of the character’s lips.
- Try not to be overdramatic and don’t “act” too much while recording. Consider anime characters as real humans with organic feelings. If you over-do it, then it can become funny and take away the gravity of the scene.
- Apart from your usual research, also watch the body language of your characters and their expressions. You can try to take the same posture and position while delivering any dialogue for a better anime dubbing experience.
- Most importantly, let the transition be more organic and feel free to make some creative choices to own the character. Remember, your aim is to be the character and not let the character become you.
- Lastly, keep in mind your audience while dubbing and make sure that they should relate to the nuances and cultural slangs you have included. While it is suggested to stick to the source material, you can bend it keeping the mindset of your target audience.
That’s a wrap, everyone! I’m sure that after reading this guide, you would be able to know more about anime dubbing and the effort that goes behind it. Although it is a complicated and tiresome process, some new-age tools and applications have made it better. If you are also just starting, then make sure you follow the above-listed tips and be familiar with the available tools. This will help you become a pro and you can certainly level-up your skills with time.

Shanoon Cox
Shanoon Cox is a writer and a lover of all things video.
Follow @Shanoon Cox
Shanoon Cox
Mar 27, 2024• Proven solutions
Anime might have been originated from Japan, but today it has become a worldwide phenomenon with millions of fans out there. Since most of the anime series are in Japanese, they are dubbed in different languages for their global audience. Though, anime dubbing is an art in itself as it takes a lot of effort to provide a seamless entertainment experience to others. In this post, I’m going to make you familiar with the process that goes behind anime dubbing and how you can master it in no time.

- Part 1: What is the Art of Anime Dubbing?
- Part 2: Why is Voicing Important in an Anime?
- Part 3: What is the Process of Anime Dubbing?
- Part 4: Is Anime Dubbing Enjoyable or Painful?
- Part 5: Anime Dubbing Tips for Beginners
What is the Art of Anime Dubbing?

http://animeyourway.blogspot.com/
There are tons of anime out there, but most of them are originally made in Japanese. To make them appealing to an international audience, the concepts of dubbing and subbing are implemented. In subbing, we simply add subtitles to the scene by placing its strip at the bottom, which is comparatively easier.
On the other hand, Anime dubbing is a more complex process in which the original soundtrack in Japanese is first removed from the video. Now, a script is designed for the other language (like English) in which the video has to be dubbed. Afterward, voiceover artists would match the dialogues with the original pace of the video to attain flawless dubbing results. Now, the audience of the second language can also watch the anime with the dubbed soundtrack instead of the Japanese.
In some cases, even after dubbing, subtitles are also added in post-production to get better results.
Why is Voicing Important in an Anime?

Anime is an art-form and hence, it is should be treated creatively when transitioning into different cultures. The first generation of anime traces to the 1910s in Japan while they became mainstream with Astro Boy that was a hit not only in Japan but in the US as well. Needless to say, the anime industry has grown drastically with over $17 billion worth worldwide.
That’s why it has become more important than ever to focus on anime dubbing and make the content appealing to a vast audience. Too many times, while dubbing, the original nature of a character is lost due to the improper voice transition. Sometimes, there are edits in the script to match the pace of the scene that ends up changing the meaning drastically.
Therefore, to make sure the true essence of the anime is maintained, the concept of voice interpretation is implemented. In this, voiceover artists are taught about their characters and their nature. Instead of bringing their own flair while recording, they are encouraged to voice their characters instead.
What is the Process of Anime Dubbing?
Now when you know the importance of anime dubbing, let’s get to know about the process in detail. Although the overall process can be implemented differently in various countries and studios, the following steps are mostly followed by professionals.
Step 1: Transitioning and Translation
This is the foundation of anime dubbing as it helps us in scriptwriting and voiceover. Firstly, the anime is studied by the team, which includes native Japanese experts. For instance, if the anime is about Japanese history or its pop culture, then an expert from the related field is asked to join.
Furthermore, all the dialogues are transcribed and further translated by professionals. To make sure that no cultural norms are lost in the process, a group of people is invited to work on this. If the anime is about pop culture, then it can be a bit tough since some dialogues might lose the original meaning in the translation.
Step 2: Scripting and Adaptation
A mere translation of the anime is not enough as it is needed to fit the scene and should have a flawless transition. For this, scriptwriters take the translated document (for instance, Japanese to English translated version) and start developing a script for that. They will watch the scene simultaneously and would work with voiceover artists as well. In this way, we can avoid any delay or rapid movement between the picture and voiceover audio.
- The new dialogues should be spoken in the same way so that the original speech and the voiceover should be matched.
- A lot of sentences have to be reconstructed entirely since Japanese grammar is pretty different than English. Sometimes, a single word in Japanese might mean a whole sentence in English. This means we need to write the script while matching the pace of the scene and keeping the meaning intact (which can be pretty challenging).
- Scriptwriters need to focus on the way a sentence is delivered and conveyed. If you are not careful, then you will lose out on certain nuances.
- To get an ideal script, you might need to watch the anime and deliver your dialogues back-and-forth. Writers are encouraged to be more adaptive and keep the cultural knowledge of their audience in mind as well.
- If the anime is deeply rooted in Japanese cultural norms that you know your audience won’t understand, then you can abandon it while still being faithful to the original material. For instance, Shin-chan had too many Japanese norms and thus it was re-written in English to include more local terms.
Step 3: Recording and Finishing
After completing the scriptwriting, recording artists work on it to give it a final touch. Although it is recommended for all recording artists to do their voice work together for a seamless amalgamation, sometimes they record their dialogues separately as well.
The recording artists are encouraged to do their bit of research and are made familiar with the anime. During the recording process, artists focus on the “matching flap” movement, which means their dialogues should match with the movement of their character’s lips. For this, they can fasten or slow their speed of dialogue delivery or add bits and pieces in between to give it a personal character.
While it is not possible to be entirely accurate and match the pace, artists try their best by looking at the video while delivering their dialogues. Some mistakes and flubs are bound to happen in the process, but that is what makes anime dubbing so hilarious and creative.
Is Anime Dubbing Enjoyable or Painful?
This is something that a lot of anime fans would like to ask voiceover professionals. Well, it would be subjective and depend on the anime as well as the professionals working on it.
In most of the cases, the process is pretty enjoyable if the artists and writers are fans of anime. Yes, the process can be a bit tedious, but that is the demand of this challenging profession altogether.
Michael Lindsay, who was widely appreciated for his work in the Marmalade Boy, admits how tough the job can be. It requires a lot of rework and the voiceover artists need to go back-and-forth to get the right pace.
Olivia Venegas, who has been a part of the anime dubbing industry for over a decade, admits how the process has changed. Now, production houses are more focused on creating a “localized” version of the anime that their audience can understand instead of keeping it rigid to their original material.
Overall, the change in the anime dubbing process and the presence of better technology has certainly made it more fun and less painful.
Anime Dubbing Tips for Beginners
If you are just starting your career in anime dubbing and would like to improve your work, then consider these expert tips.
- To start with, do your bit of research and make sure you understand the Japanese culture. If the anime is about history or a cultural phenomenon, then get to know about it so that you won’t miss any nuance.
- If you are a voiceover artist, then sit with the scriptwriter during the translation and writing process. This will help you understand their writing process and you can also give suggestions regarding voiceover.
- Focus on your speech and the pace while recording every word. At times, we are needed to eat some words or have to stretch them to match with the movement of the character’s lips.
- Try not to be overdramatic and don’t “act” too much while recording. Consider anime characters as real humans with organic feelings. If you over-do it, then it can become funny and take away the gravity of the scene.
- Apart from your usual research, also watch the body language of your characters and their expressions. You can try to take the same posture and position while delivering any dialogue for a better anime dubbing experience.
- Most importantly, let the transition be more organic and feel free to make some creative choices to own the character. Remember, your aim is to be the character and not let the character become you.
- Lastly, keep in mind your audience while dubbing and make sure that they should relate to the nuances and cultural slangs you have included. While it is suggested to stick to the source material, you can bend it keeping the mindset of your target audience.
That’s a wrap, everyone! I’m sure that after reading this guide, you would be able to know more about anime dubbing and the effort that goes behind it. Although it is a complicated and tiresome process, some new-age tools and applications have made it better. If you are also just starting, then make sure you follow the above-listed tips and be familiar with the available tools. This will help you become a pro and you can certainly level-up your skills with time.

Shanoon Cox
Shanoon Cox is a writer and a lover of all things video.
Follow @Shanoon Cox
Shanoon Cox
Mar 27, 2024• Proven solutions
Anime might have been originated from Japan, but today it has become a worldwide phenomenon with millions of fans out there. Since most of the anime series are in Japanese, they are dubbed in different languages for their global audience. Though, anime dubbing is an art in itself as it takes a lot of effort to provide a seamless entertainment experience to others. In this post, I’m going to make you familiar with the process that goes behind anime dubbing and how you can master it in no time.

- Part 1: What is the Art of Anime Dubbing?
- Part 2: Why is Voicing Important in an Anime?
- Part 3: What is the Process of Anime Dubbing?
- Part 4: Is Anime Dubbing Enjoyable or Painful?
- Part 5: Anime Dubbing Tips for Beginners
What is the Art of Anime Dubbing?

http://animeyourway.blogspot.com/
There are tons of anime out there, but most of them are originally made in Japanese. To make them appealing to an international audience, the concepts of dubbing and subbing are implemented. In subbing, we simply add subtitles to the scene by placing its strip at the bottom, which is comparatively easier.
On the other hand, Anime dubbing is a more complex process in which the original soundtrack in Japanese is first removed from the video. Now, a script is designed for the other language (like English) in which the video has to be dubbed. Afterward, voiceover artists would match the dialogues with the original pace of the video to attain flawless dubbing results. Now, the audience of the second language can also watch the anime with the dubbed soundtrack instead of the Japanese.
In some cases, even after dubbing, subtitles are also added in post-production to get better results.
Why is Voicing Important in an Anime?

Anime is an art-form and hence, it is should be treated creatively when transitioning into different cultures. The first generation of anime traces to the 1910s in Japan while they became mainstream with Astro Boy that was a hit not only in Japan but in the US as well. Needless to say, the anime industry has grown drastically with over $17 billion worth worldwide.
That’s why it has become more important than ever to focus on anime dubbing and make the content appealing to a vast audience. Too many times, while dubbing, the original nature of a character is lost due to the improper voice transition. Sometimes, there are edits in the script to match the pace of the scene that ends up changing the meaning drastically.
Therefore, to make sure the true essence of the anime is maintained, the concept of voice interpretation is implemented. In this, voiceover artists are taught about their characters and their nature. Instead of bringing their own flair while recording, they are encouraged to voice their characters instead.
What is the Process of Anime Dubbing?
Now when you know the importance of anime dubbing, let’s get to know about the process in detail. Although the overall process can be implemented differently in various countries and studios, the following steps are mostly followed by professionals.
Step 1: Transitioning and Translation
This is the foundation of anime dubbing as it helps us in scriptwriting and voiceover. Firstly, the anime is studied by the team, which includes native Japanese experts. For instance, if the anime is about Japanese history or its pop culture, then an expert from the related field is asked to join.
Furthermore, all the dialogues are transcribed and further translated by professionals. To make sure that no cultural norms are lost in the process, a group of people is invited to work on this. If the anime is about pop culture, then it can be a bit tough since some dialogues might lose the original meaning in the translation.
Step 2: Scripting and Adaptation
A mere translation of the anime is not enough as it is needed to fit the scene and should have a flawless transition. For this, scriptwriters take the translated document (for instance, Japanese to English translated version) and start developing a script for that. They will watch the scene simultaneously and would work with voiceover artists as well. In this way, we can avoid any delay or rapid movement between the picture and voiceover audio.
- The new dialogues should be spoken in the same way so that the original speech and the voiceover should be matched.
- A lot of sentences have to be reconstructed entirely since Japanese grammar is pretty different than English. Sometimes, a single word in Japanese might mean a whole sentence in English. This means we need to write the script while matching the pace of the scene and keeping the meaning intact (which can be pretty challenging).
- Scriptwriters need to focus on the way a sentence is delivered and conveyed. If you are not careful, then you will lose out on certain nuances.
- To get an ideal script, you might need to watch the anime and deliver your dialogues back-and-forth. Writers are encouraged to be more adaptive and keep the cultural knowledge of their audience in mind as well.
- If the anime is deeply rooted in Japanese cultural norms that you know your audience won’t understand, then you can abandon it while still being faithful to the original material. For instance, Shin-chan had too many Japanese norms and thus it was re-written in English to include more local terms.
Step 3: Recording and Finishing
After completing the scriptwriting, recording artists work on it to give it a final touch. Although it is recommended for all recording artists to do their voice work together for a seamless amalgamation, sometimes they record their dialogues separately as well.
The recording artists are encouraged to do their bit of research and are made familiar with the anime. During the recording process, artists focus on the “matching flap” movement, which means their dialogues should match with the movement of their character’s lips. For this, they can fasten or slow their speed of dialogue delivery or add bits and pieces in between to give it a personal character.
While it is not possible to be entirely accurate and match the pace, artists try their best by looking at the video while delivering their dialogues. Some mistakes and flubs are bound to happen in the process, but that is what makes anime dubbing so hilarious and creative.
Is Anime Dubbing Enjoyable or Painful?
This is something that a lot of anime fans would like to ask voiceover professionals. Well, it would be subjective and depend on the anime as well as the professionals working on it.
In most of the cases, the process is pretty enjoyable if the artists and writers are fans of anime. Yes, the process can be a bit tedious, but that is the demand of this challenging profession altogether.
Michael Lindsay, who was widely appreciated for his work in the Marmalade Boy, admits how tough the job can be. It requires a lot of rework and the voiceover artists need to go back-and-forth to get the right pace.
Olivia Venegas, who has been a part of the anime dubbing industry for over a decade, admits how the process has changed. Now, production houses are more focused on creating a “localized” version of the anime that their audience can understand instead of keeping it rigid to their original material.
Overall, the change in the anime dubbing process and the presence of better technology has certainly made it more fun and less painful.
Anime Dubbing Tips for Beginners
If you are just starting your career in anime dubbing and would like to improve your work, then consider these expert tips.
- To start with, do your bit of research and make sure you understand the Japanese culture. If the anime is about history or a cultural phenomenon, then get to know about it so that you won’t miss any nuance.
- If you are a voiceover artist, then sit with the scriptwriter during the translation and writing process. This will help you understand their writing process and you can also give suggestions regarding voiceover.
- Focus on your speech and the pace while recording every word. At times, we are needed to eat some words or have to stretch them to match with the movement of the character’s lips.
- Try not to be overdramatic and don’t “act” too much while recording. Consider anime characters as real humans with organic feelings. If you over-do it, then it can become funny and take away the gravity of the scene.
- Apart from your usual research, also watch the body language of your characters and their expressions. You can try to take the same posture and position while delivering any dialogue for a better anime dubbing experience.
- Most importantly, let the transition be more organic and feel free to make some creative choices to own the character. Remember, your aim is to be the character and not let the character become you.
- Lastly, keep in mind your audience while dubbing and make sure that they should relate to the nuances and cultural slangs you have included. While it is suggested to stick to the source material, you can bend it keeping the mindset of your target audience.
That’s a wrap, everyone! I’m sure that after reading this guide, you would be able to know more about anime dubbing and the effort that goes behind it. Although it is a complicated and tiresome process, some new-age tools and applications have made it better. If you are also just starting, then make sure you follow the above-listed tips and be familiar with the available tools. This will help you become a pro and you can certainly level-up your skills with time.

Shanoon Cox
Shanoon Cox is a writer and a lover of all things video.
Follow @Shanoon Cox
Shanoon Cox
Mar 27, 2024• Proven solutions
Anime might have been originated from Japan, but today it has become a worldwide phenomenon with millions of fans out there. Since most of the anime series are in Japanese, they are dubbed in different languages for their global audience. Though, anime dubbing is an art in itself as it takes a lot of effort to provide a seamless entertainment experience to others. In this post, I’m going to make you familiar with the process that goes behind anime dubbing and how you can master it in no time.

- Part 1: What is the Art of Anime Dubbing?
- Part 2: Why is Voicing Important in an Anime?
- Part 3: What is the Process of Anime Dubbing?
- Part 4: Is Anime Dubbing Enjoyable or Painful?
- Part 5: Anime Dubbing Tips for Beginners
What is the Art of Anime Dubbing?

http://animeyourway.blogspot.com/
There are tons of anime out there, but most of them are originally made in Japanese. To make them appealing to an international audience, the concepts of dubbing and subbing are implemented. In subbing, we simply add subtitles to the scene by placing its strip at the bottom, which is comparatively easier.
On the other hand, Anime dubbing is a more complex process in which the original soundtrack in Japanese is first removed from the video. Now, a script is designed for the other language (like English) in which the video has to be dubbed. Afterward, voiceover artists would match the dialogues with the original pace of the video to attain flawless dubbing results. Now, the audience of the second language can also watch the anime with the dubbed soundtrack instead of the Japanese.
In some cases, even after dubbing, subtitles are also added in post-production to get better results.
Why is Voicing Important in an Anime?

Anime is an art-form and hence, it is should be treated creatively when transitioning into different cultures. The first generation of anime traces to the 1910s in Japan while they became mainstream with Astro Boy that was a hit not only in Japan but in the US as well. Needless to say, the anime industry has grown drastically with over $17 billion worth worldwide.
That’s why it has become more important than ever to focus on anime dubbing and make the content appealing to a vast audience. Too many times, while dubbing, the original nature of a character is lost due to the improper voice transition. Sometimes, there are edits in the script to match the pace of the scene that ends up changing the meaning drastically.
Therefore, to make sure the true essence of the anime is maintained, the concept of voice interpretation is implemented. In this, voiceover artists are taught about their characters and their nature. Instead of bringing their own flair while recording, they are encouraged to voice their characters instead.
What is the Process of Anime Dubbing?
Now when you know the importance of anime dubbing, let’s get to know about the process in detail. Although the overall process can be implemented differently in various countries and studios, the following steps are mostly followed by professionals.
Step 1: Transitioning and Translation
This is the foundation of anime dubbing as it helps us in scriptwriting and voiceover. Firstly, the anime is studied by the team, which includes native Japanese experts. For instance, if the anime is about Japanese history or its pop culture, then an expert from the related field is asked to join.
Furthermore, all the dialogues are transcribed and further translated by professionals. To make sure that no cultural norms are lost in the process, a group of people is invited to work on this. If the anime is about pop culture, then it can be a bit tough since some dialogues might lose the original meaning in the translation.
Step 2: Scripting and Adaptation
A mere translation of the anime is not enough as it is needed to fit the scene and should have a flawless transition. For this, scriptwriters take the translated document (for instance, Japanese to English translated version) and start developing a script for that. They will watch the scene simultaneously and would work with voiceover artists as well. In this way, we can avoid any delay or rapid movement between the picture and voiceover audio.
- The new dialogues should be spoken in the same way so that the original speech and the voiceover should be matched.
- A lot of sentences have to be reconstructed entirely since Japanese grammar is pretty different than English. Sometimes, a single word in Japanese might mean a whole sentence in English. This means we need to write the script while matching the pace of the scene and keeping the meaning intact (which can be pretty challenging).
- Scriptwriters need to focus on the way a sentence is delivered and conveyed. If you are not careful, then you will lose out on certain nuances.
- To get an ideal script, you might need to watch the anime and deliver your dialogues back-and-forth. Writers are encouraged to be more adaptive and keep the cultural knowledge of their audience in mind as well.
- If the anime is deeply rooted in Japanese cultural norms that you know your audience won’t understand, then you can abandon it while still being faithful to the original material. For instance, Shin-chan had too many Japanese norms and thus it was re-written in English to include more local terms.
Step 3: Recording and Finishing
After completing the scriptwriting, recording artists work on it to give it a final touch. Although it is recommended for all recording artists to do their voice work together for a seamless amalgamation, sometimes they record their dialogues separately as well.
The recording artists are encouraged to do their bit of research and are made familiar with the anime. During the recording process, artists focus on the “matching flap” movement, which means their dialogues should match with the movement of their character’s lips. For this, they can fasten or slow their speed of dialogue delivery or add bits and pieces in between to give it a personal character.
While it is not possible to be entirely accurate and match the pace, artists try their best by looking at the video while delivering their dialogues. Some mistakes and flubs are bound to happen in the process, but that is what makes anime dubbing so hilarious and creative.
Is Anime Dubbing Enjoyable or Painful?
This is something that a lot of anime fans would like to ask voiceover professionals. Well, it would be subjective and depend on the anime as well as the professionals working on it.
In most of the cases, the process is pretty enjoyable if the artists and writers are fans of anime. Yes, the process can be a bit tedious, but that is the demand of this challenging profession altogether.
Michael Lindsay, who was widely appreciated for his work in the Marmalade Boy, admits how tough the job can be. It requires a lot of rework and the voiceover artists need to go back-and-forth to get the right pace.
Olivia Venegas, who has been a part of the anime dubbing industry for over a decade, admits how the process has changed. Now, production houses are more focused on creating a “localized” version of the anime that their audience can understand instead of keeping it rigid to their original material.
Overall, the change in the anime dubbing process and the presence of better technology has certainly made it more fun and less painful.
Anime Dubbing Tips for Beginners
If you are just starting your career in anime dubbing and would like to improve your work, then consider these expert tips.
- To start with, do your bit of research and make sure you understand the Japanese culture. If the anime is about history or a cultural phenomenon, then get to know about it so that you won’t miss any nuance.
- If you are a voiceover artist, then sit with the scriptwriter during the translation and writing process. This will help you understand their writing process and you can also give suggestions regarding voiceover.
- Focus on your speech and the pace while recording every word. At times, we are needed to eat some words or have to stretch them to match with the movement of the character’s lips.
- Try not to be overdramatic and don’t “act” too much while recording. Consider anime characters as real humans with organic feelings. If you over-do it, then it can become funny and take away the gravity of the scene.
- Apart from your usual research, also watch the body language of your characters and their expressions. You can try to take the same posture and position while delivering any dialogue for a better anime dubbing experience.
- Most importantly, let the transition be more organic and feel free to make some creative choices to own the character. Remember, your aim is to be the character and not let the character become you.
- Lastly, keep in mind your audience while dubbing and make sure that they should relate to the nuances and cultural slangs you have included. While it is suggested to stick to the source material, you can bend it keeping the mindset of your target audience.
That’s a wrap, everyone! I’m sure that after reading this guide, you would be able to know more about anime dubbing and the effort that goes behind it. Although it is a complicated and tiresome process, some new-age tools and applications have made it better. If you are also just starting, then make sure you follow the above-listed tips and be familiar with the available tools. This will help you become a pro and you can certainly level-up your skills with time.

Shanoon Cox
Shanoon Cox is a writer and a lover of all things video.
Follow @Shanoon Cox
Elevating Audio Excellence: Adjusting Pitch in Audacity without Compromising Quality
You may raise or lower the pitch of a pre-recorded song. Likewise, you may apply the pitch-changing effect in real-time sound recording. Change in pitch affects your noise in certain ways. For instance, it can help you sound younger. Similarly, it can convert the male voice into a female voice. Another notable use of the pitch-changing technique is that you can produce sounds like cartoons. So, changing pitch can add a unique touch to your voice. You can also change pitch when recording in Audacity. The following article covers details about the Audacity change pitch feature. Let’s get started.
In this article
01 What is pitch, and how does it work?
02 How to Change Pitch in Audacity?
Part 1: What is pitch, and how does it work?
Not all sounds are the same. Some vary in terms of amplitude, which makes them loud or quiet. In contrast, others vary in terms of pitch, which makes them high or low. Pitch is used to differentiate between the acute and flat notes in a sound wave. High-pitched sounds are likely to be shrilling, whereas the lower-pitched will be bassy. Pitch depends upon the frequency of the sound waves producing them. In short, notes at a higher frequency are high-pitched.
On the contrary, notes at lower frequencies are low-pitched. Changing a pitch of noise from low to high or vice versa is an art. Thus, sound recording and editing applications like Audacity come with the in-built effect that enables you to change the pitch of a sound.
Part 2: How to Change Pitch in Audacity?
Sound editing is becoming increasingly popular in music and other relevant industries. Several applications offer sound editing tools to serve the needs of the people. Pitch-changing is one of the common tools that people look for in sound editors.
Audacity is one of the notable software that allows users to change the pitch of the voice. It comes with an Audacity pitch shift mechanism to facilitate users. So, if you are editing sound in Audacity, changing the pitch is just a matter of a few clicks. Are you still wondering how you can apply the Audacity change pitch technique when editing? Here’s how you can do it in simple steps.
Step 1: Select the audio portion
Launch Audacity and add sound recordings you want to edit. Click on the timeline and drag to select the portion of the sound.
Note: Only the portion whose pitch you want to change.
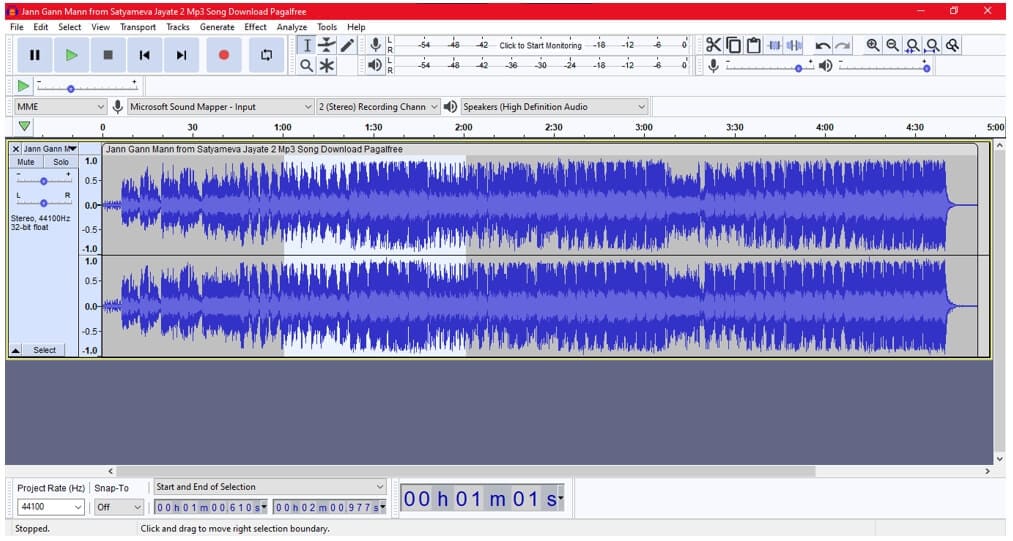
Step 2: Open Effect menu
Click on the Effect tab at the top right of the screen next to Generate. Select Pitch Change from the drop-down menu.
Note: You can also make other changes, such as Change Speed and Change Tempo option will let you alter the speed of the sound. So, the pitch can also be altered using this process.
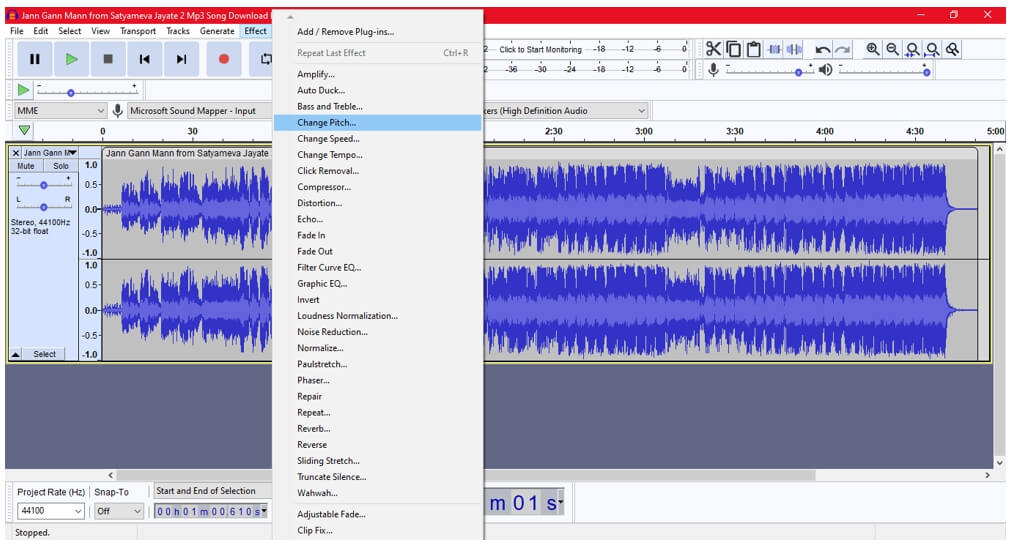
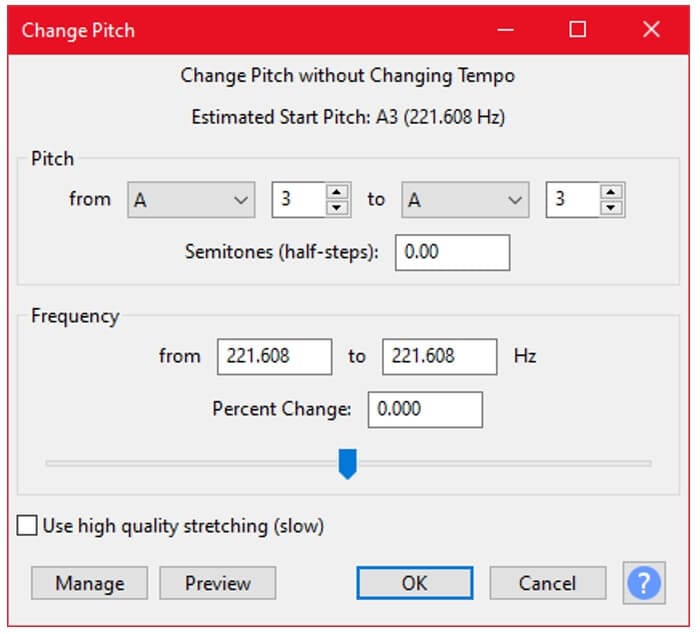
Step 3: Adjust pitch
Drag the slider to alter the pitch of the sound and press the OK button to apply changes.
Note: To increase pitch, slide towards the right. Similarly, slide towards the left to a lower pitch. In addition, the pitch can also be changed by configuring From and To parameters.
Bonus Section: How to Adjust Sound Louder in Audacity?
Volume in an audio file may or may not be ideal for use. Sometimes, the sound is too loud or low. Audacity can help you in such a situation. So, if you are editing sound recordings in Audacity, you can also fix the volume of the sound. The good thing to note is that you can adjust the sound in both directions, which implies you can easily amplify or reduce the volume in these open-source applications. Are you interested in knowing about the volume adjustment process in Audacity? If yes, we have summarized the process in simple steps. Let’s take a look.
Step 1: Add an audio file
Launch the software and click on File. Select Open and select the desired audio.
Note: It is not recommended to change the volume through the playback volume knob at the top right corner of the screen, as this will only increase the volume in your device. However, the actual volume of the audio will remain unchanged.
Step 2: Increase/Decrease audio gain
Change the gain of the audio at the left-hand side of the screen. Move the slider to adjust the volume to the desired level.
Note: Alternatively, you may also increase or increase the volume through the amplification process. To use this method, select the audio portion, access Effect, and tap Amplify. Tick allow clipping box and move the slider to set the volume of the sound.
Conclusion
There are high chances of audio sound not being in the required pitch or volume. Plus, you may also need to change the sound characteristics of an audio file for specific use. So, if this is the case, the Audacity change pitch technique is all you need to learn. Thus, we have summarized the process of changing pitch and volume in a step-by-step guide in this article. Hopefully, all your concerns will have been addressed.
02 How to Change Pitch in Audacity?
Part 1: What is pitch, and how does it work?
Not all sounds are the same. Some vary in terms of amplitude, which makes them loud or quiet. In contrast, others vary in terms of pitch, which makes them high or low. Pitch is used to differentiate between the acute and flat notes in a sound wave. High-pitched sounds are likely to be shrilling, whereas the lower-pitched will be bassy. Pitch depends upon the frequency of the sound waves producing them. In short, notes at a higher frequency are high-pitched.
On the contrary, notes at lower frequencies are low-pitched. Changing a pitch of noise from low to high or vice versa is an art. Thus, sound recording and editing applications like Audacity come with the in-built effect that enables you to change the pitch of a sound.
Part 2: How to Change Pitch in Audacity?
Sound editing is becoming increasingly popular in music and other relevant industries. Several applications offer sound editing tools to serve the needs of the people. Pitch-changing is one of the common tools that people look for in sound editors.
Audacity is one of the notable software that allows users to change the pitch of the voice. It comes with an Audacity pitch shift mechanism to facilitate users. So, if you are editing sound in Audacity, changing the pitch is just a matter of a few clicks. Are you still wondering how you can apply the Audacity change pitch technique when editing? Here’s how you can do it in simple steps.
Step 1: Select the audio portion
Launch Audacity and add sound recordings you want to edit. Click on the timeline and drag to select the portion of the sound.
Note: Only the portion whose pitch you want to change.

Step 2: Open Effect menu
Click on the Effect tab at the top right of the screen next to Generate. Select Pitch Change from the drop-down menu.
Note: You can also make other changes, such as Change Speed and Change Tempo option will let you alter the speed of the sound. So, the pitch can also be altered using this process.

Step 3: Adjust pitch
Drag the slider to alter the pitch of the sound and press the OK button to apply changes.
Note: To increase pitch, slide towards the right. Similarly, slide towards the left to a lower pitch. In addition, the pitch can also be changed by configuring From and To parameters.

Bonus Section: How to Adjust Sound Louder in Audacity?
Volume in an audio file may or may not be ideal for use. Sometimes, the sound is too loud or low. Audacity can help you in such a situation. So, if you are editing sound recordings in Audacity, you can also fix the volume of the sound. The good thing to note is that you can adjust the sound in both directions, which implies you can easily amplify or reduce the volume in these open-source applications. Are you interested in knowing about the volume adjustment process in Audacity? If yes, we have summarized the process in simple steps. Let’s take a look.
Step 1: Add an audio file
Launch the software and click on File. Select Open and select the desired audio.
Note: It is not recommended to change the volume through the playback volume knob at the top right corner of the screen, as this will only increase the volume in your device. However, the actual volume of the audio will remain unchanged.

Step 2: Increase/Decrease audio gain
Change the gain of the audio at the left-hand side of the screen. Move the slider to adjust the volume to the desired level.

Note: Alternatively, you may also increase or increase the volume through the amplification process. To use this method, select the audio portion, access Effect, and tap Amplify. Tick allow clipping box and move the slider to set the volume of the sound.
Conclusion
There are high chances of audio sound not being in the required pitch or volume. Plus, you may also need to change the sound characteristics of an audio file for specific use. So, if this is the case, the Audacity change pitch technique is all you need to learn. Thus, we have summarized the process of changing pitch and volume in a step-by-step guide in this article. Hopefully, all your concerns will have been addressed.
02 How to Change Pitch in Audacity?
Part 1: What is pitch, and how does it work?
Not all sounds are the same. Some vary in terms of amplitude, which makes them loud or quiet. In contrast, others vary in terms of pitch, which makes them high or low. Pitch is used to differentiate between the acute and flat notes in a sound wave. High-pitched sounds are likely to be shrilling, whereas the lower-pitched will be bassy. Pitch depends upon the frequency of the sound waves producing them. In short, notes at a higher frequency are high-pitched.
On the contrary, notes at lower frequencies are low-pitched. Changing a pitch of noise from low to high or vice versa is an art. Thus, sound recording and editing applications like Audacity come with the in-built effect that enables you to change the pitch of a sound.
Part 2: How to Change Pitch in Audacity?
Sound editing is becoming increasingly popular in music and other relevant industries. Several applications offer sound editing tools to serve the needs of the people. Pitch-changing is one of the common tools that people look for in sound editors.
Audacity is one of the notable software that allows users to change the pitch of the voice. It comes with an Audacity pitch shift mechanism to facilitate users. So, if you are editing sound in Audacity, changing the pitch is just a matter of a few clicks. Are you still wondering how you can apply the Audacity change pitch technique when editing? Here’s how you can do it in simple steps.
Step 1: Select the audio portion
Launch Audacity and add sound recordings you want to edit. Click on the timeline and drag to select the portion of the sound.
Note: Only the portion whose pitch you want to change.

Step 2: Open Effect menu
Click on the Effect tab at the top right of the screen next to Generate. Select Pitch Change from the drop-down menu.
Note: You can also make other changes, such as Change Speed and Change Tempo option will let you alter the speed of the sound. So, the pitch can also be altered using this process.

Step 3: Adjust pitch
Drag the slider to alter the pitch of the sound and press the OK button to apply changes.
Note: To increase pitch, slide towards the right. Similarly, slide towards the left to a lower pitch. In addition, the pitch can also be changed by configuring From and To parameters.

Bonus Section: How to Adjust Sound Louder in Audacity?
Volume in an audio file may or may not be ideal for use. Sometimes, the sound is too loud or low. Audacity can help you in such a situation. So, if you are editing sound recordings in Audacity, you can also fix the volume of the sound. The good thing to note is that you can adjust the sound in both directions, which implies you can easily amplify or reduce the volume in these open-source applications. Are you interested in knowing about the volume adjustment process in Audacity? If yes, we have summarized the process in simple steps. Let’s take a look.
Step 1: Add an audio file
Launch the software and click on File. Select Open and select the desired audio.
Note: It is not recommended to change the volume through the playback volume knob at the top right corner of the screen, as this will only increase the volume in your device. However, the actual volume of the audio will remain unchanged.

Step 2: Increase/Decrease audio gain
Change the gain of the audio at the left-hand side of the screen. Move the slider to adjust the volume to the desired level.

Note: Alternatively, you may also increase or increase the volume through the amplification process. To use this method, select the audio portion, access Effect, and tap Amplify. Tick allow clipping box and move the slider to set the volume of the sound.
Conclusion
There are high chances of audio sound not being in the required pitch or volume. Plus, you may also need to change the sound characteristics of an audio file for specific use. So, if this is the case, the Audacity change pitch technique is all you need to learn. Thus, we have summarized the process of changing pitch and volume in a step-by-step guide in this article. Hopefully, all your concerns will have been addressed.
02 How to Change Pitch in Audacity?
Part 1: What is pitch, and how does it work?
Not all sounds are the same. Some vary in terms of amplitude, which makes them loud or quiet. In contrast, others vary in terms of pitch, which makes them high or low. Pitch is used to differentiate between the acute and flat notes in a sound wave. High-pitched sounds are likely to be shrilling, whereas the lower-pitched will be bassy. Pitch depends upon the frequency of the sound waves producing them. In short, notes at a higher frequency are high-pitched.
On the contrary, notes at lower frequencies are low-pitched. Changing a pitch of noise from low to high or vice versa is an art. Thus, sound recording and editing applications like Audacity come with the in-built effect that enables you to change the pitch of a sound.
Part 2: How to Change Pitch in Audacity?
Sound editing is becoming increasingly popular in music and other relevant industries. Several applications offer sound editing tools to serve the needs of the people. Pitch-changing is one of the common tools that people look for in sound editors.
Audacity is one of the notable software that allows users to change the pitch of the voice. It comes with an Audacity pitch shift mechanism to facilitate users. So, if you are editing sound in Audacity, changing the pitch is just a matter of a few clicks. Are you still wondering how you can apply the Audacity change pitch technique when editing? Here’s how you can do it in simple steps.
Step 1: Select the audio portion
Launch Audacity and add sound recordings you want to edit. Click on the timeline and drag to select the portion of the sound.
Note: Only the portion whose pitch you want to change.

Step 2: Open Effect menu
Click on the Effect tab at the top right of the screen next to Generate. Select Pitch Change from the drop-down menu.
Note: You can also make other changes, such as Change Speed and Change Tempo option will let you alter the speed of the sound. So, the pitch can also be altered using this process.

Step 3: Adjust pitch
Drag the slider to alter the pitch of the sound and press the OK button to apply changes.
Note: To increase pitch, slide towards the right. Similarly, slide towards the left to a lower pitch. In addition, the pitch can also be changed by configuring From and To parameters.

Bonus Section: How to Adjust Sound Louder in Audacity?
Volume in an audio file may or may not be ideal for use. Sometimes, the sound is too loud or low. Audacity can help you in such a situation. So, if you are editing sound recordings in Audacity, you can also fix the volume of the sound. The good thing to note is that you can adjust the sound in both directions, which implies you can easily amplify or reduce the volume in these open-source applications. Are you interested in knowing about the volume adjustment process in Audacity? If yes, we have summarized the process in simple steps. Let’s take a look.
Step 1: Add an audio file
Launch the software and click on File. Select Open and select the desired audio.
Note: It is not recommended to change the volume through the playback volume knob at the top right corner of the screen, as this will only increase the volume in your device. However, the actual volume of the audio will remain unchanged.

Step 2: Increase/Decrease audio gain
Change the gain of the audio at the left-hand side of the screen. Move the slider to adjust the volume to the desired level.

Note: Alternatively, you may also increase or increase the volume through the amplification process. To use this method, select the audio portion, access Effect, and tap Amplify. Tick allow clipping box and move the slider to set the volume of the sound.
Conclusion
There are high chances of audio sound not being in the required pitch or volume. Plus, you may also need to change the sound characteristics of an audio file for specific use. So, if this is the case, the Audacity change pitch technique is all you need to learn. Thus, we have summarized the process of changing pitch and volume in a step-by-step guide in this article. Hopefully, all your concerns will have been addressed.
The Audio Experts’ Manual to Identifying Superior Sound Formats
How to Choose Best Audio Formats

Benjamin Arango
Mar 27, 2024• Proven solutions
The quality of sound that you hear depends on various factors, and an appropriate audio format is one of them. While each type of acoustic file has its own significance, choosing the best audio format as per the target player, expected audience, and/or supporting videos or images (if any) is something that needs much consideration to offer a flawless listening experience.
With that said, here you will learn about some of the most common sound file types, which among them could be the best audio format according to your requirements, and a couple of important points that you must keep in might while picking an extension for your media preparations.
- Part 1: 10 Most Common Audio Formats
- Part 2: How to Choose Best Audio Format?
- Part 3: Which Audio File Formats Does YouTube Support?
- Part 4: Audio Format in Filmora
Using Filmora to Record & Edit & Save Audio Easily
Wondershare Filmora is a simple yet robust video editing software that allows you to save a video to mp3 easily. Besides, if you want to remove background noise from audio, or change the audio volume or remove unwanted audio parts from the video, you should definitely try Filmora.
Part 1: 10 Most Common Audio Formats
Before listing the most common audio file formats, it is important to understand the categories of the sound files. Every audio format that exists belongs to one (or more) category depending on the way it is being created and the characteristics it has.
In a nutshell, there are three major categories, including:
- Uncompressed Audio Format
- Lossless Compressed Audio Format
- Lossy Compressed Audio Format
Below is a brief introduction of each of the classes listed above along with the audio file types that belong to them:
1. Uncompressed Audio Format
Uncompressed audio is the original sound that has been recorded directly from the source in the analog form, and then converted to a digital signal without any modifications or compressions. Because an uncompressed sound is prepared with no retouching or manipulations, it gives an as-is listening experience. Since no compression is done on such a file either, it occupies a remarkably huge amount of space on your storage media.
Some sound files that fall under this category include:
1) Pulse-Code Modulation (PCM)
A PCM file is the digital version of an analog waveform that is created by recording the audio samples, technically known as pulses. The PCM format is mostly used when creating optical media discs, typically the CDs and DVDs.
2) Waveform Audio File Format (WAV)
Generally used on the Windows platform, this audio format is not a file itself but a container that may contain both compressed or uncompressed files. However, in most cases, it is the latter that a WAV file has, and PCM format is one of them.
You may also interest: YouTube to WAV >>
3) Audio Interchange File Format (AIFF)
AIFF is almost identical to WAV format in its characteristics with the only difference that, unlike the latter, it was developed by Apple somewhere in 1988, and works as a container for both compressed and uncompressed audio files. While the compressed version of the format is called AIFF-C, the term Apple Loop is used when the scenario is otherwise. As it is with WAV, even AIFF files mostly contain uncompressed audio, that usually is PCM.
You may also like: Best AIFF to MP3 Converters >>
4) Data Stream Digital (DSD)
Used by Sony and Phillips, DSD is also not a format itself but a container that can store PCM files to provide decent sound quality. However, due to distortions in the composed audio, DSD files are not much in trend.
2. Lossless Compressed Audio Format
Lossless Compressed audio format is a type of file that is compressed using some advanced methods without compromising with the quality of the sound. This means that when played, you experience the same acoustic excellence as that of the source, i.e. uncompressed audio. However, even though the lossless compressed files are comparatively small in size, they still occupy decent amount of space on the hard drive or any other storage media in use.
Some formats that fall under the lossless compressed category include:
1) Free Lossless Audio Code (FLAC)
At around half the size of the source sound file, FLAC offers the original audio quality without removing any acoustic information during compression. Being an opensource and royalty-free audio format, FLAC is even easier to get, and in most cases is used as an alternative to MP3.
Check some of the best FLAC editor programs >>
2) Apple Lossless Audio Codec (ALAC)
Introduced by Apple Inc. and initially released as a proprietary product, ALAC was made royalty-free and opensource in 2011. Even though ALAC files are larger in size when compared to FLAC, the former format is used in iTunes and iOS as the latter isn’t supported by these platforms.
3. Lossy Compressed Audio Format
These are the highly compressed files that occupy significantly less amount of space on your storage media. However, during the compression process, some acoustic information is lost in order to reduce the file size. Nevertheless, if compressed correctly, the deterioration in the quality is almost negligible, and cannot be experienced unless the listener is quite experienced and the source recording is played next to the compressed audio simultaneously.
Some audio formats that fall under the lossy compressed category include:
1) MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 (MP3)
This is one of the most common file types and the best audio format for almost all media types that have sound. An MP3 file is free from the noises of the least significant in the composed audio. In addition, all the acoustic information with the frequency that normal human beings fail to catch (below 20Hz and above 20000Hz) is safely erased during compilation and compression. Furthermore, what makes MP3 the best audio file format is its ability to accommodate with almost all the devices of nearly any platform such as Android, Windows, iOS, Mac, etc.
Check this MP3 editor and convert video to MP3 easily.
2) OGG
This one, again, is not in fact an audio format but is a container for audio that generally stores Vorbis files. Although OGG files are way advanced in terms of sound quality and even offer higher compression ratio when compared with MP3, they are not much in use as many platforms and devices don’t support the format till date.
3) AU
AU is a format by Sun, DEC, and NeXT. It is yet another container that can hold both lossless and lossy files. AU files are mostly used in UNIX.
What’s the difference between common audio file formats like MP3, WAV, and FLAC? Watch the video below to learn more.
Part 2: How to Choose Best Audio Format?
If you are a media creator, and are into the business of preparing audio and video content for your clients or directly for the audience, it is imperative to understand what could be the best audio file format to compose the audiovisual files. Here are a few tips that you must keep in mind in this context before proceeding:
- Uncompressed Audio
If the media type you are about to create is expected to be used for further editing before exporting to a different format, using an uncompressed audio format would be best as it offers a smooth and flawless post-production experience without giving much overhead to the processor.
- Lossless Compressed Audio
If your audiences own highly sophisticated audio players with Hi-Fi speaker systems, and they are also good at recognizing and understanding the differences between poor and optimal audio quality, using lossless compressed audio format would be a good choice as it gives decent sound quality in smaller file size.
- Compressed Audio
If you are preparing a media for home users and casual listeners, you can safely use an audio format that has been prepared using a higher compression ratio. In such a scenario, MP3 is the best audio format that not only offers the decent sound quality, it also occupies less amount of space on your storage media, thus enabling you to save more files at a given time.
Part 3: Which Audio File Formats Does YouTube Support?
At the time of this writing, YouTube supports two types of formats namely MPEG-2 and MPEG-4. Although both of these are video containers, they also hold audio files. Details about both these types are as follows:
- MPEG-2
- Audio Bitrate: 128kbps or above
- Audio Codec: Dolby AC-3 or MPEG Layer II
- MPEG-4
- **Video Codec:**264
- Audio Bitrate: 128kbps or above
Since many people nowadays produce videos in MP4 due to its wide range of supported devices and players and the fact that the container is used by majority of users worldwide, MPEG-4 with audio format could be mostly seen on YouTube.
Part 4: Audio Format in Filmora
Being one of the most versatile post-production tools preferred by many professional editors worldwide, Filmora comes with a variety of audio formats from all the three categories discussed above. Furthermore, Filmora also displays relevant information about each of the file types it offers.
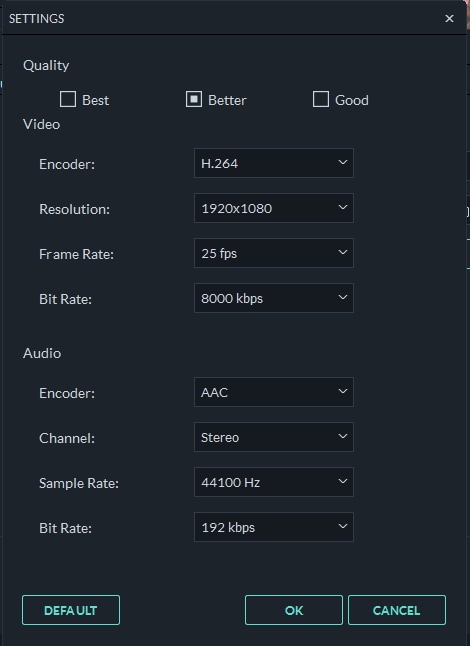
The following table shows a list of formats and the details that Filmora supports:
| Video Format | Corresponding Audio Encoder | Audio Type |
|---|---|---|
| MP4 | Lossy Compressed | |
| WMV | WMA8, WMA9 | Uncompressed |
| AVI | MP3, PCM | Lossy Compressed, Uncompressed |
| MOV | Lossy Compressed | |
| F4V | Lossy Compressed | |
| MKV | MP3 | Lossy Compressed |
| TS | MPEG-2 Audio | Lossy Compressed |
| 3GP | Lossy Compressed | |
| MPEG-2 | MPEG-2 Audio | Lossy Compressed |
| WEBM | Vorbis | Lossy Compressed |

Benjamin Arango
Benjamin Arango is a writer and a lover of all things video.
Follow @Benjamin Arango
Benjamin Arango
Mar 27, 2024• Proven solutions
The quality of sound that you hear depends on various factors, and an appropriate audio format is one of them. While each type of acoustic file has its own significance, choosing the best audio format as per the target player, expected audience, and/or supporting videos or images (if any) is something that needs much consideration to offer a flawless listening experience.
With that said, here you will learn about some of the most common sound file types, which among them could be the best audio format according to your requirements, and a couple of important points that you must keep in might while picking an extension for your media preparations.
- Part 1: 10 Most Common Audio Formats
- Part 2: How to Choose Best Audio Format?
- Part 3: Which Audio File Formats Does YouTube Support?
- Part 4: Audio Format in Filmora
Using Filmora to Record & Edit & Save Audio Easily
Wondershare Filmora is a simple yet robust video editing software that allows you to save a video to mp3 easily. Besides, if you want to remove background noise from audio, or change the audio volume or remove unwanted audio parts from the video, you should definitely try Filmora.
Part 1: 10 Most Common Audio Formats
Before listing the most common audio file formats, it is important to understand the categories of the sound files. Every audio format that exists belongs to one (or more) category depending on the way it is being created and the characteristics it has.
In a nutshell, there are three major categories, including:
- Uncompressed Audio Format
- Lossless Compressed Audio Format
- Lossy Compressed Audio Format
Below is a brief introduction of each of the classes listed above along with the audio file types that belong to them:
1. Uncompressed Audio Format
Uncompressed audio is the original sound that has been recorded directly from the source in the analog form, and then converted to a digital signal without any modifications or compressions. Because an uncompressed sound is prepared with no retouching or manipulations, it gives an as-is listening experience. Since no compression is done on such a file either, it occupies a remarkably huge amount of space on your storage media.
Some sound files that fall under this category include:
1) Pulse-Code Modulation (PCM)
A PCM file is the digital version of an analog waveform that is created by recording the audio samples, technically known as pulses. The PCM format is mostly used when creating optical media discs, typically the CDs and DVDs.
2) Waveform Audio File Format (WAV)
Generally used on the Windows platform, this audio format is not a file itself but a container that may contain both compressed or uncompressed files. However, in most cases, it is the latter that a WAV file has, and PCM format is one of them.
You may also interest: YouTube to WAV >>
3) Audio Interchange File Format (AIFF)
AIFF is almost identical to WAV format in its characteristics with the only difference that, unlike the latter, it was developed by Apple somewhere in 1988, and works as a container for both compressed and uncompressed audio files. While the compressed version of the format is called AIFF-C, the term Apple Loop is used when the scenario is otherwise. As it is with WAV, even AIFF files mostly contain uncompressed audio, that usually is PCM.
You may also like: Best AIFF to MP3 Converters >>
4) Data Stream Digital (DSD)
Used by Sony and Phillips, DSD is also not a format itself but a container that can store PCM files to provide decent sound quality. However, due to distortions in the composed audio, DSD files are not much in trend.
2. Lossless Compressed Audio Format
Lossless Compressed audio format is a type of file that is compressed using some advanced methods without compromising with the quality of the sound. This means that when played, you experience the same acoustic excellence as that of the source, i.e. uncompressed audio. However, even though the lossless compressed files are comparatively small in size, they still occupy decent amount of space on the hard drive or any other storage media in use.
Some formats that fall under the lossless compressed category include:
1) Free Lossless Audio Code (FLAC)
At around half the size of the source sound file, FLAC offers the original audio quality without removing any acoustic information during compression. Being an opensource and royalty-free audio format, FLAC is even easier to get, and in most cases is used as an alternative to MP3.
Check some of the best FLAC editor programs >>
2) Apple Lossless Audio Codec (ALAC)
Introduced by Apple Inc. and initially released as a proprietary product, ALAC was made royalty-free and opensource in 2011. Even though ALAC files are larger in size when compared to FLAC, the former format is used in iTunes and iOS as the latter isn’t supported by these platforms.
3. Lossy Compressed Audio Format
These are the highly compressed files that occupy significantly less amount of space on your storage media. However, during the compression process, some acoustic information is lost in order to reduce the file size. Nevertheless, if compressed correctly, the deterioration in the quality is almost negligible, and cannot be experienced unless the listener is quite experienced and the source recording is played next to the compressed audio simultaneously.
Some audio formats that fall under the lossy compressed category include:
1) MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 (MP3)
This is one of the most common file types and the best audio format for almost all media types that have sound. An MP3 file is free from the noises of the least significant in the composed audio. In addition, all the acoustic information with the frequency that normal human beings fail to catch (below 20Hz and above 20000Hz) is safely erased during compilation and compression. Furthermore, what makes MP3 the best audio file format is its ability to accommodate with almost all the devices of nearly any platform such as Android, Windows, iOS, Mac, etc.
Check this MP3 editor and convert video to MP3 easily.
2) OGG
This one, again, is not in fact an audio format but is a container for audio that generally stores Vorbis files. Although OGG files are way advanced in terms of sound quality and even offer higher compression ratio when compared with MP3, they are not much in use as many platforms and devices don’t support the format till date.
3) AU
AU is a format by Sun, DEC, and NeXT. It is yet another container that can hold both lossless and lossy files. AU files are mostly used in UNIX.
What’s the difference between common audio file formats like MP3, WAV, and FLAC? Watch the video below to learn more.
Part 2: How to Choose Best Audio Format?
If you are a media creator, and are into the business of preparing audio and video content for your clients or directly for the audience, it is imperative to understand what could be the best audio file format to compose the audiovisual files. Here are a few tips that you must keep in mind in this context before proceeding:
- Uncompressed Audio
If the media type you are about to create is expected to be used for further editing before exporting to a different format, using an uncompressed audio format would be best as it offers a smooth and flawless post-production experience without giving much overhead to the processor.
- Lossless Compressed Audio
If your audiences own highly sophisticated audio players with Hi-Fi speaker systems, and they are also good at recognizing and understanding the differences between poor and optimal audio quality, using lossless compressed audio format would be a good choice as it gives decent sound quality in smaller file size.
- Compressed Audio
If you are preparing a media for home users and casual listeners, you can safely use an audio format that has been prepared using a higher compression ratio. In such a scenario, MP3 is the best audio format that not only offers the decent sound quality, it also occupies less amount of space on your storage media, thus enabling you to save more files at a given time.
Part 3: Which Audio File Formats Does YouTube Support?
At the time of this writing, YouTube supports two types of formats namely MPEG-2 and MPEG-4. Although both of these are video containers, they also hold audio files. Details about both these types are as follows:
- MPEG-2
- Audio Bitrate: 128kbps or above
- Audio Codec: Dolby AC-3 or MPEG Layer II
- MPEG-4
- **Video Codec:**264
- Audio Bitrate: 128kbps or above
Since many people nowadays produce videos in MP4 due to its wide range of supported devices and players and the fact that the container is used by majority of users worldwide, MPEG-4 with audio format could be mostly seen on YouTube.
Part 4: Audio Format in Filmora
Being one of the most versatile post-production tools preferred by many professional editors worldwide, Filmora comes with a variety of audio formats from all the three categories discussed above. Furthermore, Filmora also displays relevant information about each of the file types it offers.

The following table shows a list of formats and the details that Filmora supports:
| Video Format | Corresponding Audio Encoder | Audio Type |
|---|---|---|
| MP4 | Lossy Compressed | |
| WMV | WMA8, WMA9 | Uncompressed |
| AVI | MP3, PCM | Lossy Compressed, Uncompressed |
| MOV | Lossy Compressed | |
| F4V | Lossy Compressed | |
| MKV | MP3 | Lossy Compressed |
| TS | MPEG-2 Audio | Lossy Compressed |
| 3GP | Lossy Compressed | |
| MPEG-2 | MPEG-2 Audio | Lossy Compressed |
| WEBM | Vorbis | Lossy Compressed |

Benjamin Arango
Benjamin Arango is a writer and a lover of all things video.
Follow @Benjamin Arango
Benjamin Arango
Mar 27, 2024• Proven solutions
The quality of sound that you hear depends on various factors, and an appropriate audio format is one of them. While each type of acoustic file has its own significance, choosing the best audio format as per the target player, expected audience, and/or supporting videos or images (if any) is something that needs much consideration to offer a flawless listening experience.
With that said, here you will learn about some of the most common sound file types, which among them could be the best audio format according to your requirements, and a couple of important points that you must keep in might while picking an extension for your media preparations.
- Part 1: 10 Most Common Audio Formats
- Part 2: How to Choose Best Audio Format?
- Part 3: Which Audio File Formats Does YouTube Support?
- Part 4: Audio Format in Filmora
Using Filmora to Record & Edit & Save Audio Easily
Wondershare Filmora is a simple yet robust video editing software that allows you to save a video to mp3 easily. Besides, if you want to remove background noise from audio, or change the audio volume or remove unwanted audio parts from the video, you should definitely try Filmora.
Part 1: 10 Most Common Audio Formats
Before listing the most common audio file formats, it is important to understand the categories of the sound files. Every audio format that exists belongs to one (or more) category depending on the way it is being created and the characteristics it has.
In a nutshell, there are three major categories, including:
- Uncompressed Audio Format
- Lossless Compressed Audio Format
- Lossy Compressed Audio Format
Below is a brief introduction of each of the classes listed above along with the audio file types that belong to them:
1. Uncompressed Audio Format
Uncompressed audio is the original sound that has been recorded directly from the source in the analog form, and then converted to a digital signal without any modifications or compressions. Because an uncompressed sound is prepared with no retouching or manipulations, it gives an as-is listening experience. Since no compression is done on such a file either, it occupies a remarkably huge amount of space on your storage media.
Some sound files that fall under this category include:
1) Pulse-Code Modulation (PCM)
A PCM file is the digital version of an analog waveform that is created by recording the audio samples, technically known as pulses. The PCM format is mostly used when creating optical media discs, typically the CDs and DVDs.
2) Waveform Audio File Format (WAV)
Generally used on the Windows platform, this audio format is not a file itself but a container that may contain both compressed or uncompressed files. However, in most cases, it is the latter that a WAV file has, and PCM format is one of them.
You may also interest: YouTube to WAV >>
3) Audio Interchange File Format (AIFF)
AIFF is almost identical to WAV format in its characteristics with the only difference that, unlike the latter, it was developed by Apple somewhere in 1988, and works as a container for both compressed and uncompressed audio files. While the compressed version of the format is called AIFF-C, the term Apple Loop is used when the scenario is otherwise. As it is with WAV, even AIFF files mostly contain uncompressed audio, that usually is PCM.
You may also like: Best AIFF to MP3 Converters >>
4) Data Stream Digital (DSD)
Used by Sony and Phillips, DSD is also not a format itself but a container that can store PCM files to provide decent sound quality. However, due to distortions in the composed audio, DSD files are not much in trend.
2. Lossless Compressed Audio Format
Lossless Compressed audio format is a type of file that is compressed using some advanced methods without compromising with the quality of the sound. This means that when played, you experience the same acoustic excellence as that of the source, i.e. uncompressed audio. However, even though the lossless compressed files are comparatively small in size, they still occupy decent amount of space on the hard drive or any other storage media in use.
Some formats that fall under the lossless compressed category include:
1) Free Lossless Audio Code (FLAC)
At around half the size of the source sound file, FLAC offers the original audio quality without removing any acoustic information during compression. Being an opensource and royalty-free audio format, FLAC is even easier to get, and in most cases is used as an alternative to MP3.
Check some of the best FLAC editor programs >>
2) Apple Lossless Audio Codec (ALAC)
Introduced by Apple Inc. and initially released as a proprietary product, ALAC was made royalty-free and opensource in 2011. Even though ALAC files are larger in size when compared to FLAC, the former format is used in iTunes and iOS as the latter isn’t supported by these platforms.
3. Lossy Compressed Audio Format
These are the highly compressed files that occupy significantly less amount of space on your storage media. However, during the compression process, some acoustic information is lost in order to reduce the file size. Nevertheless, if compressed correctly, the deterioration in the quality is almost negligible, and cannot be experienced unless the listener is quite experienced and the source recording is played next to the compressed audio simultaneously.
Some audio formats that fall under the lossy compressed category include:
1) MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 (MP3)
This is one of the most common file types and the best audio format for almost all media types that have sound. An MP3 file is free from the noises of the least significant in the composed audio. In addition, all the acoustic information with the frequency that normal human beings fail to catch (below 20Hz and above 20000Hz) is safely erased during compilation and compression. Furthermore, what makes MP3 the best audio file format is its ability to accommodate with almost all the devices of nearly any platform such as Android, Windows, iOS, Mac, etc.
Check this MP3 editor and convert video to MP3 easily.
2) OGG
This one, again, is not in fact an audio format but is a container for audio that generally stores Vorbis files. Although OGG files are way advanced in terms of sound quality and even offer higher compression ratio when compared with MP3, they are not much in use as many platforms and devices don’t support the format till date.
3) AU
AU is a format by Sun, DEC, and NeXT. It is yet another container that can hold both lossless and lossy files. AU files are mostly used in UNIX.
What’s the difference between common audio file formats like MP3, WAV, and FLAC? Watch the video below to learn more.
Part 2: How to Choose Best Audio Format?
If you are a media creator, and are into the business of preparing audio and video content for your clients or directly for the audience, it is imperative to understand what could be the best audio file format to compose the audiovisual files. Here are a few tips that you must keep in mind in this context before proceeding:
- Uncompressed Audio
If the media type you are about to create is expected to be used for further editing before exporting to a different format, using an uncompressed audio format would be best as it offers a smooth and flawless post-production experience without giving much overhead to the processor.
- Lossless Compressed Audio
If your audiences own highly sophisticated audio players with Hi-Fi speaker systems, and they are also good at recognizing and understanding the differences between poor and optimal audio quality, using lossless compressed audio format would be a good choice as it gives decent sound quality in smaller file size.
- Compressed Audio
If you are preparing a media for home users and casual listeners, you can safely use an audio format that has been prepared using a higher compression ratio. In such a scenario, MP3 is the best audio format that not only offers the decent sound quality, it also occupies less amount of space on your storage media, thus enabling you to save more files at a given time.
Part 3: Which Audio File Formats Does YouTube Support?
At the time of this writing, YouTube supports two types of formats namely MPEG-2 and MPEG-4. Although both of these are video containers, they also hold audio files. Details about both these types are as follows:
- MPEG-2
- Audio Bitrate: 128kbps or above
- Audio Codec: Dolby AC-3 or MPEG Layer II
- MPEG-4
- **Video Codec:**264
- Audio Bitrate: 128kbps or above
Since many people nowadays produce videos in MP4 due to its wide range of supported devices and players and the fact that the container is used by majority of users worldwide, MPEG-4 with audio format could be mostly seen on YouTube.
Part 4: Audio Format in Filmora
Being one of the most versatile post-production tools preferred by many professional editors worldwide, Filmora comes with a variety of audio formats from all the three categories discussed above. Furthermore, Filmora also displays relevant information about each of the file types it offers.

The following table shows a list of formats and the details that Filmora supports:
| Video Format | Corresponding Audio Encoder | Audio Type |
|---|---|---|
| MP4 | Lossy Compressed | |
| WMV | WMA8, WMA9 | Uncompressed |
| AVI | MP3, PCM | Lossy Compressed, Uncompressed |
| MOV | Lossy Compressed | |
| F4V | Lossy Compressed | |
| MKV | MP3 | Lossy Compressed |
| TS | MPEG-2 Audio | Lossy Compressed |
| 3GP | Lossy Compressed | |
| MPEG-2 | MPEG-2 Audio | Lossy Compressed |
| WEBM | Vorbis | Lossy Compressed |

Benjamin Arango
Benjamin Arango is a writer and a lover of all things video.
Follow @Benjamin Arango
Benjamin Arango
Mar 27, 2024• Proven solutions
The quality of sound that you hear depends on various factors, and an appropriate audio format is one of them. While each type of acoustic file has its own significance, choosing the best audio format as per the target player, expected audience, and/or supporting videos or images (if any) is something that needs much consideration to offer a flawless listening experience.
With that said, here you will learn about some of the most common sound file types, which among them could be the best audio format according to your requirements, and a couple of important points that you must keep in might while picking an extension for your media preparations.
- Part 1: 10 Most Common Audio Formats
- Part 2: How to Choose Best Audio Format?
- Part 3: Which Audio File Formats Does YouTube Support?
- Part 4: Audio Format in Filmora
Using Filmora to Record & Edit & Save Audio Easily
Wondershare Filmora is a simple yet robust video editing software that allows you to save a video to mp3 easily. Besides, if you want to remove background noise from audio, or change the audio volume or remove unwanted audio parts from the video, you should definitely try Filmora.
Part 1: 10 Most Common Audio Formats
Before listing the most common audio file formats, it is important to understand the categories of the sound files. Every audio format that exists belongs to one (or more) category depending on the way it is being created and the characteristics it has.
In a nutshell, there are three major categories, including:
- Uncompressed Audio Format
- Lossless Compressed Audio Format
- Lossy Compressed Audio Format
Below is a brief introduction of each of the classes listed above along with the audio file types that belong to them:
1. Uncompressed Audio Format
Uncompressed audio is the original sound that has been recorded directly from the source in the analog form, and then converted to a digital signal without any modifications or compressions. Because an uncompressed sound is prepared with no retouching or manipulations, it gives an as-is listening experience. Since no compression is done on such a file either, it occupies a remarkably huge amount of space on your storage media.
Some sound files that fall under this category include:
1) Pulse-Code Modulation (PCM)
A PCM file is the digital version of an analog waveform that is created by recording the audio samples, technically known as pulses. The PCM format is mostly used when creating optical media discs, typically the CDs and DVDs.
2) Waveform Audio File Format (WAV)
Generally used on the Windows platform, this audio format is not a file itself but a container that may contain both compressed or uncompressed files. However, in most cases, it is the latter that a WAV file has, and PCM format is one of them.
You may also interest: YouTube to WAV >>
3) Audio Interchange File Format (AIFF)
AIFF is almost identical to WAV format in its characteristics with the only difference that, unlike the latter, it was developed by Apple somewhere in 1988, and works as a container for both compressed and uncompressed audio files. While the compressed version of the format is called AIFF-C, the term Apple Loop is used when the scenario is otherwise. As it is with WAV, even AIFF files mostly contain uncompressed audio, that usually is PCM.
You may also like: Best AIFF to MP3 Converters >>
4) Data Stream Digital (DSD)
Used by Sony and Phillips, DSD is also not a format itself but a container that can store PCM files to provide decent sound quality. However, due to distortions in the composed audio, DSD files are not much in trend.
2. Lossless Compressed Audio Format
Lossless Compressed audio format is a type of file that is compressed using some advanced methods without compromising with the quality of the sound. This means that when played, you experience the same acoustic excellence as that of the source, i.e. uncompressed audio. However, even though the lossless compressed files are comparatively small in size, they still occupy decent amount of space on the hard drive or any other storage media in use.
Some formats that fall under the lossless compressed category include:
1) Free Lossless Audio Code (FLAC)
At around half the size of the source sound file, FLAC offers the original audio quality without removing any acoustic information during compression. Being an opensource and royalty-free audio format, FLAC is even easier to get, and in most cases is used as an alternative to MP3.
Check some of the best FLAC editor programs >>
2) Apple Lossless Audio Codec (ALAC)
Introduced by Apple Inc. and initially released as a proprietary product, ALAC was made royalty-free and opensource in 2011. Even though ALAC files are larger in size when compared to FLAC, the former format is used in iTunes and iOS as the latter isn’t supported by these platforms.
3. Lossy Compressed Audio Format
These are the highly compressed files that occupy significantly less amount of space on your storage media. However, during the compression process, some acoustic information is lost in order to reduce the file size. Nevertheless, if compressed correctly, the deterioration in the quality is almost negligible, and cannot be experienced unless the listener is quite experienced and the source recording is played next to the compressed audio simultaneously.
Some audio formats that fall under the lossy compressed category include:
1) MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 (MP3)
This is one of the most common file types and the best audio format for almost all media types that have sound. An MP3 file is free from the noises of the least significant in the composed audio. In addition, all the acoustic information with the frequency that normal human beings fail to catch (below 20Hz and above 20000Hz) is safely erased during compilation and compression. Furthermore, what makes MP3 the best audio file format is its ability to accommodate with almost all the devices of nearly any platform such as Android, Windows, iOS, Mac, etc.
Check this MP3 editor and convert video to MP3 easily.
2) OGG
This one, again, is not in fact an audio format but is a container for audio that generally stores Vorbis files. Although OGG files are way advanced in terms of sound quality and even offer higher compression ratio when compared with MP3, they are not much in use as many platforms and devices don’t support the format till date.
3) AU
AU is a format by Sun, DEC, and NeXT. It is yet another container that can hold both lossless and lossy files. AU files are mostly used in UNIX.
What’s the difference between common audio file formats like MP3, WAV, and FLAC? Watch the video below to learn more.
Part 2: How to Choose Best Audio Format?
If you are a media creator, and are into the business of preparing audio and video content for your clients or directly for the audience, it is imperative to understand what could be the best audio file format to compose the audiovisual files. Here are a few tips that you must keep in mind in this context before proceeding:
- Uncompressed Audio
If the media type you are about to create is expected to be used for further editing before exporting to a different format, using an uncompressed audio format would be best as it offers a smooth and flawless post-production experience without giving much overhead to the processor.
- Lossless Compressed Audio
If your audiences own highly sophisticated audio players with Hi-Fi speaker systems, and they are also good at recognizing and understanding the differences between poor and optimal audio quality, using lossless compressed audio format would be a good choice as it gives decent sound quality in smaller file size.
- Compressed Audio
If you are preparing a media for home users and casual listeners, you can safely use an audio format that has been prepared using a higher compression ratio. In such a scenario, MP3 is the best audio format that not only offers the decent sound quality, it also occupies less amount of space on your storage media, thus enabling you to save more files at a given time.
Part 3: Which Audio File Formats Does YouTube Support?
At the time of this writing, YouTube supports two types of formats namely MPEG-2 and MPEG-4. Although both of these are video containers, they also hold audio files. Details about both these types are as follows:
- MPEG-2
- Audio Bitrate: 128kbps or above
- Audio Codec: Dolby AC-3 or MPEG Layer II
- MPEG-4
- **Video Codec:**264
- Audio Bitrate: 128kbps or above
Since many people nowadays produce videos in MP4 due to its wide range of supported devices and players and the fact that the container is used by majority of users worldwide, MPEG-4 with audio format could be mostly seen on YouTube.
Part 4: Audio Format in Filmora
Being one of the most versatile post-production tools preferred by many professional editors worldwide, Filmora comes with a variety of audio formats from all the three categories discussed above. Furthermore, Filmora also displays relevant information about each of the file types it offers.

The following table shows a list of formats and the details that Filmora supports:
| Video Format | Corresponding Audio Encoder | Audio Type |
|---|---|---|
| MP4 | Lossy Compressed | |
| WMV | WMA8, WMA9 | Uncompressed |
| AVI | MP3, PCM | Lossy Compressed, Uncompressed |
| MOV | Lossy Compressed | |
| F4V | Lossy Compressed | |
| MKV | MP3 | Lossy Compressed |
| TS | MPEG-2 Audio | Lossy Compressed |
| 3GP | Lossy Compressed | |
| MPEG-2 | MPEG-2 Audio | Lossy Compressed |
| WEBM | Vorbis | Lossy Compressed |

Benjamin Arango
Benjamin Arango is a writer and a lover of all things video.
Follow @Benjamin Arango
Also read:
- Updated 2024 Approved Harmonizing Screens A List of the Top 15 Scores for Various Genre Videos
- New In 2024, Mastering iPhone Audio Recordings A Detailed Tutorial
- Harmony Extractor Purify Your Medias Acoustic Environment
- New In 2024, Hear the World on a Budget Discover Free Music Downloads Today
- New Silent Stream Sculptors Crafting Audience-Free Video Formats (MP4, MKV, AVI, MOV, WMV) for 2024
- New Mastering the Aesthetics of Audio Design Examining Features, Benefits, Drawbacks, and Comparisons with Alternatives
- Updated 2024 Approved Beyond Vocaroo A Guide to Audio Capture Techniques and Alternative Tools
- Updated Free & Frugal Mac MP3 Optimizer App
- New In 2024, The Modern Guide to Integrating Visuals with Sound Audio Enhancement
- Updated Hunting for Genuine Creature Roar Ambience
- Updated Virtual Meow Melody Mixer for 2024
- Social Strategy Sessions The Top 2023 List of Podcast Episodes for Brands
- New Discover the Impact of Bristle Movement Noise for 2024
- New The Ultimate List of Free-to-Download Montage Music Sites
- Best Windows 10 Auditory Integration Software Compared
- Updated 2024 Approved The Ultimate List of Free BGM Music Streaming Sites, Updated
- New 2024 Approved FREE MUSIC Integration Into Digital Photography on PC/Mobile Devices
- Updated 2024 Approved The Essential Directory of Fee-Free, High-Quality Audio Player Applications for Android and iOS Devices
- New 2024 Approved Mastering GarageBand A Comprehensive Tutorial for Recording Music
- Updated 2024 Approved Uncover Leading Software Options for Isolating Sound in Multimedia Projects
- Unique Vocal Plugins for Zoom The Top 6 Apps That Make Your Conversations Memorable for 2024
- Updated In 2024, Easy Voice Modification Utilities Functions and Comparisons
- Updated Sneak Peek Into the Secret of Silent Videos in Windows 10 (No Additional Software) for 2024
- Updated From Chatter to Silence Utilizing iMovie for Superior Sound Filtration
- Updated 2024 Approved Exploring the Horizon of Audio Transcription Technologies
- New The Art of Voice Customization on Audacity for Professionals
- In 2024, The Ultimate Selection of Windows-Friendly Speech Conversion Software
- New 6 Best Voice Changer During Call Android & iPhone
- 2024 Approved Best Alternatives to VirtualDub Video Processing Software Compared
- How to Unlock Apple iPhone SE (2022) Passcode without Computer?
- 2 Ways to Transfer Text Messages from Oppo A1 5G to iPhone 15/14/13/12/11/X/8/ | Dr.fone
- Updated Do You Want to Know About Phone Aspect Ratio Vertical? Trying to Learn About iPhone Vertical Video Dimensions? Read This Article to Get All Your Answers on Vertical Phone Aspect Ratio Definition, Types and Tips
- Updated 2024 Approved The Ultimate List Top-Rated Free 3GP Video Rotators
- How to Use Pokémon Emerald Master Ball Cheat On Honor 90 GT | Dr.fone
- In 2024, How to Transfer Apps from Infinix Note 30 VIP to Another | Dr.fone
- 2024 Approved Stream the Hottest Trailers Top 10 iPhone and iPad Movie Apps
- A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering iPogo for Pokémon GO On Apple iPhone X | Dr.fone
- In 2024, How To Fix Auto Lock Greyed Out on iPhone 12 Pro | Dr.fone
- In 2024, Easy Ways to Manage Your Oppo Find N3 Flip Location Settings | Dr.fone
- How To Get the Apple ID Verification Code On Apple iPhone 12 Pro in the Best Ways
- Things You Dont Know About Infinix Hot 40 Pro Reset Code | Dr.fone
- How Do You Get Sun Stone Evolutions in Pokémon For Vivo Y56 5G? | Dr.fone
- Updated 2024 Approved Best Film Trailer Editing Tools for Mac and Windows Users
- Unlock ZTE Blade A73 5G Phone Password Without Factory Reset Full Guide Here
- Updated In 2024, Elevate Your Video Game Top Online Editors for Chromebook
- In 2024, How To Create an Apple Developer Account On iPhone SE (2022)
- How to Share Location in Messenger On Oppo F23 5G? | Dr.fone
- The Ultimate Guide to Get the Rare Candy on Pokemon Go Fire Red On Apple iPhone 12 | Dr.fone
- How do i sign a Word 2013 free
- This is how you can recover deleted pictures from Google .
- Full Guide to Catch 100 IV Pokémon Using a Map On Itel A05s | Dr.fone
- 2024 Approved Bring Your Vision to Life 7 Best Movie Intro Design Software
- 2024 Approved Top 16 Free Video Editing Software for Beginners Very Easy to Use
- Title: New 2024 Approved All About Anime Dubbing
- Author: David
- Created at : 2024-05-05 09:50:10
- Updated at : 2024-05-06 09:50:10
- Link: https://sound-tweaking.techidaily.com/new-2024-approved-all-about-anime-dubbing/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.